Top Cloud Infrastructure Automation Tools for DevOps 2025
Discover the best cloud infrastructure automation tools to streamline your DevOps processes in 2025. Boost efficiency with expert-selected solutions.
In modern software delivery, manual infrastructure management is a critical bottleneck. It introduces configuration drift, is prone to human error, and cannot scale with the demands of CI/CD pipelines. The solution is Infrastructure as Code (IaC), a practice that manages and provisions infrastructure through version-controlled, machine-readable definition files. This article serves as a comprehensive technical guide to the leading cloud infrastructure automation tools that enable this practice, helping you select the right engine for your DevOps stack.
We move beyond surface-level feature lists to provide an in-depth analysis of each platform. You'll find detailed comparisons, practical use-case scenarios, and technical assessments of limitations to inform your decision-making process. This guide is designed for technical leaders, platform engineers, and DevOps professionals who need to make strategic choices about their infrastructure management, whether they are building a scalable startup or optimizing enterprise-level continuous delivery workflows.
This resource specifically focuses on tools for provisioning and managing core infrastructure. For a broader overview of various solutions that cover the entire continuous delivery pipeline, from version control to monitoring, you can explore these Top DevOps Automation Tools for 2025.
Here, we will dissect twelve powerful options, from declarative IaC frameworks like Terraform and Pulumi to configuration management giants like Ansible and Chef, and managed control planes like Upbound. Each entry includes direct links and screenshots to give you a clear, actionable understanding of its capabilities. Our goal is to equip you with the insights needed to choose the tool that best fits your team’s programming language preferences, cloud provider strategy, and operational complexity. Let’s dive into the core components that will automate and scale your cloud environment.
1. IBM HashiCorp Cloud Platform (HCP Terraform / Terraform Cloud)
HCP Terraform, formerly Terraform Cloud, is a managed service that provides a consistent workflow for teams to provision infrastructure as code across any cloud. As one of the most established cloud infrastructure automation tools, it excels at collaborative state management, policy enforcement, and integrating with version control systems like Git to trigger automated infrastructure deployments. Its primary strength lies in creating a centralized, auditable source of truth for your entire infrastructure lifecycle via a remote backend.
This platform is ideal for enterprise teams standardizing on Terraform, offering features that enable scale and governance. The central state management prevents conflicts and state file corruption common when teams manually share terraform.tfstate files. Its policy-as-code framework, Sentinel, allows you to enforce fine-grained rules on infrastructure changes during the terraform plan phase, ensuring compliance with security baselines and cost-control policies before terraform apply is ever executed.
Key Considerations
The platform's user experience is streamlined for a GitOps workflow, where infrastructure changes are managed through pull requests that trigger speculative plans for review.
| Feature | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Usage-based pricing on resources under management (RUM). While flexible, it can be unpredictable for dynamic environments where resources are frequently created and destroyed. |
| Deployment Options | Available as a SaaS offering (HCP Terraform) or a self-managed version (Terraform Enterprise) for organizations requiring maximum control over their data and environment. |
| Ecosystem & Integration | Boasts the broadest provider support in the industry, enabling management of nearly any service. The public module registry significantly accelerates development. |
| Licensing | The shift from an open-source license to the Business Source License (BUSL 1.1) in 2023 for its core may be a factor for organizations with strict open-source software policies. |
Practical Tip: To manage costs effectively under the RUM model, implement strict lifecycle policies to automatically destroy temporary or unused resources, especially in development and testing environments. You can learn more about how to leverage HashiCorp's platform for scalable infrastructure management.
Website: https://www.hashicorp.com/pricing
2. Pulumi (IaC + Pulumi Cloud)
Pulumi differentiates itself by enabling developers to define and manage cloud infrastructure using familiar, general-purpose programming languages like TypeScript, Python, and Go. This approach makes it one of the most developer-centric cloud infrastructure automation tools, allowing teams to leverage existing language features like loops, conditionals, and classes to build complex infrastructure. The managed Pulumi Cloud service acts as the control plane, providing state management, policy enforcement, and deployment visibility.
This platform is particularly effective for teams looking to unify their application and infrastructure codebases. Instead of learning a separate domain-specific language (DSL), developers can use the same tools, IDEs, and testing frameworks for both application logic and the infrastructure it runs on. Pulumi Cloud enhances this with features like Pulumi Insights, which provides a searchable resource inventory for auditing, compliance checks, and cost analysis across all your cloud environments.
Key Considerations
Pulumi's user experience is designed to integrate seamlessly into a software development lifecycle, allowing for robust testing and abstraction patterns not easily achieved with DSL-based tools.
| Feature | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Pricing Model | A generous free tier for individuals is available. Paid tiers are priced per-resource (Pulumi credits), which can be complex to forecast for highly dynamic or large-scale environments, requiring careful budget estimation. |
| Deployment Options | Offered primarily as a SaaS solution (Pulumi Cloud). A self-hosted Business Edition is available for enterprises needing to keep all state and operational data within their own network boundaries. |
| Ecosystem & Integration | Supports all major cloud providers and a growing number of services. Its ability to use any language package manager (e.g., npm, pip) allows for powerful code sharing and reuse, though its community module ecosystem is smaller than Terraform's. |
| Licensing | The core Pulumi SDK is open source under the Apache 2.0 license, which is a permissive and widely accepted license, making it a safe choice for most organizations. |
Practical Tip: Leverage your chosen programming language's testing frameworks (e.g., Jest for TypeScript, Pytest for Python) to write unit and integration tests for your infrastructure code. This helps catch errors before deployment, a significant advantage of Pulumi’s approach. You can find detailed implementation patterns by reviewing various infrastructure-as-code examples.
Website: https://www.pulumi.com/pricing/
3. AWS CloudFormation
AWS CloudFormation is the native infrastructure as code (IaC) service for the Amazon Web Services ecosystem. As a foundational cloud infrastructure automation tool, it enables you to model, provision, and manage a collection of related AWS and third-party resources declaratively using templates. Its core strength is its unparalleled, deep integration with the AWS platform, providing day-one support for new services and features, ensuring a cohesive management experience.
This platform is the default choice for teams heavily invested in the AWS cloud who need reliable, integrated, and auditable infrastructure management. Features like change sets allow you to preview the impact of template modifications before execution, preventing unintended resource disruption. Furthermore, drift detection helps identify out-of-band changes, ensuring your deployed infrastructure state always matches the template's definition. StackSets extend this capability, allowing you to provision and manage stacks across multiple AWS accounts and regions from a single operation.
Key Considerations
CloudFormation templates, written in YAML or JSON, become the single source of truth for your AWS environment, integrating seamlessly with services like AWS CodePipeline for CI/CD automation.
| Feature | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Pricing Model | There is no additional charge for CloudFormation itself when managing native AWS resources. You only pay for the AWS resources provisioned. However, charges apply for handler operations on third-party resources managed via the CloudFormation Registry after a generous free tier. |
| Deployment Options | A fully managed AWS service, tightly integrated with the AWS Management Console, CLI, and SDKs. There is no self-hosted option, as its functionality is intrinsically tied to the AWS control plane. |
| Ecosystem & Integration | Offers the most comprehensive support for AWS services. The CloudFormation Registry extends functionality to manage third-party resources and modules, including providers from Datadog, MongoDB Atlas, and others, although the ecosystem is less extensive than Terraform's. |
| Licensing | A proprietary service from AWS. While templates are user-owned, the underlying engine and service are not open-source, which can be a consideration for teams prioritizing open standards for multi-cloud portability. |
Practical Tip: Use CloudFormation StackSets to enforce standardized security and logging configurations (e.g., AWS Config rules, IAM roles, CloudTrail) across all accounts in your AWS Organization. This centralizes governance and ensures baseline compliance from a single template.
Website: https://aws.amazon.com/cloudformation/pricing/
4. Microsoft Azure Bicep (ARM)
Azure Bicep is a domain-specific language (DSL) that serves as a transparent abstraction over Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates. It simplifies the authoring experience for deploying Azure resources declaratively. As one of the native cloud infrastructure automation tools for the Azure ecosystem, it provides a cleaner syntax, strong typing, and modularity, which directly compiles to standard ARM JSON, ensuring immediate support for all new Azure services from day one.
The platform is designed for teams deeply invested in the Microsoft cloud, offering a more readable and maintainable alternative to raw JSON. Bicep's core advantage is its state management model; unlike other tools that require a separate state file, Azure itself acts as the source of truth, simplifying operations and reducing the risk of state drift. This tight integration provides a seamless developer experience within tools like Visual Studio Code, with rich IntelliSense and validation.
Key Considerations
Bicep enhances ARM's capabilities with a 'what-if' operation, allowing teams to preview changes before applying them, which is critical for preventing unintended modifications in production environments. While Bicep provides a declarative approach, imperative automation remains vital for specific tasks. For example, understanding programmatic control, such as provisioning Azure VMs with PowerShell, can complement a Bicep workflow for complex, multi-step deployments.
| Feature | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Completely free to use. Costs are incurred only for the Azure resources you provision and manage, with no additional licensing fees for the Bicep language or tooling itself. |
| Deployment Options | Bicep is not a hosted service; it is a language and a set of tools (CLI, VS Code extension) that you use to generate ARM templates for deployment via Azure CLI or PowerShell. |
| Ecosystem & Integration | Native integration with Azure DevOps and GitHub Actions for CI/CD pipelines. While the module ecosystem is growing, it is less extensive than Terraform's public registry. |
| Vendor Lock-In | Designed exclusively for the Azure platform. This single-cloud focus is a significant limitation for organizations operating in multi-cloud or hybrid environments. |
Practical Tip: Use Bicep's decompilation feature (az bicep decompile) on existing ARM templates exported from the Azure portal. This is an excellent way to learn the Bicep syntax and rapidly convert your existing JSON-based infrastructure into more maintainable Bicep code.
Website: https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-resource-manager/bicep/overview
5. Google Cloud Infrastructure Manager (for Terraform)
Google Cloud Infrastructure Manager is a managed service designed to automate and orchestrate Terraform deployments natively within the Google Cloud ecosystem. As a dedicated cloud infrastructure automation tool for GCP, it leverages familiar services like Cloud Build and Cloud Storage to provide a streamlined, GitOps-centric workflow. The service simplifies the process of managing GCP resources by providing a centralized and automated execution environment directly within the platform you are provisioning.
Its core strength lies in its seamless integration with the GCP environment. It uses your existing IAM permissions, billing, and observability tools, eliminating the need to configure a separate, third-party platform. This native approach is ideal for teams deeply invested in Google Cloud who want to adopt infrastructure as code without introducing external dependencies or complex security configurations.
Key Considerations
The platform is purpose-built for GCP, meaning the user experience is tightly coupled with the Google Cloud Console and its associated services.
| Feature | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Follows a clear, pay-as-you-go model based on Cloud Build execution minutes and Cloud Storage usage. Costs are predictable and consolidated into your existing GCP bill. |
| Deployment Options | This is a fully managed SaaS offering within Google Cloud. There is no self-managed or on-premises version, as its value is derived from its native integration. |
| Ecosystem & Integration | Natively integrates with GCP services and IAM. While compatible with the broader Terraform ecosystem (providers, modules), its primary focus and automation triggers are GCP-centric. |
| Licensing | The service itself is proprietary to Google Cloud, but it executes standard, open-source Terraform, making it compatible with configurations using various license types. |
Practical Tip: To enhance security, leverage Infrastructure Manager's ability to use a service account for deployments. This allows you to grant fine-grained, least-privilege IAM permissions for Terraform runs, ensuring your infrastructure changes are executed within a controlled and auditable security context.
Website: https://cloud.google.com/infrastructure-manager/pricing
6. Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform is an enterprise-grade solution that extends the power of open-source Ansible into a comprehensive framework for provisioning, configuration management, and application deployment. It stands out as one of the most versatile cloud infrastructure automation tools by combining an agentless architecture with a simple, human-readable YAML syntax. The platform excels at orchestrating complex workflows across hybrid cloud environments, from initial server provisioning to ongoing compliance and configuration drift management.
This platform is particularly well-suited for organizations with significant investments in Linux and traditional IT infrastructure alongside their cloud-native services. Its strength lies in providing a unified automation language that bridges the gap between different teams and technology stacks. Features like the Automation Hub, with its certified and supported content collections, provide a secure and reliable way to scale automation efforts, while Event-Driven Ansible allows for proactive, self-healing infrastructure that responds to real-time events from monitoring tools.
Key Considerations
The platform's focus on operational simplicity and its extensive module library make it a powerful tool for both infrastructure provisioning and day-two operations.
| Feature | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Quote-based and dependent on the number of managed nodes. This requires careful capacity planning and direct engagement with Red Hat sales to determine costs. |
| Deployment Options | Available as a self-managed installation for on-premises or private cloud, and also offered as a managed service on major cloud marketplaces like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. |
| Ecosystem & Integration | Boasts a massive ecosystem of modules and collections for managing everything from network devices and Linux servers to cloud services and Windows systems. Event-Driven Ansible integrates with sources like Kafka and cloud provider events. |
| Learning Curve | While Ansible's core syntax is easy to learn, mastering best practices for large-scale, idempotent playbook development and inventory management presents a steeper learning curve for advanced use cases. |
Practical Tip: Leverage the Automation Hub to use certified content collections. These pre-built, supported modules and roles reduce development time and ensure your automation is built on a stable, secure foundation, which is crucial for production environments.
Website: https://www.redhat.com/en/technologies/management/ansible/pricing
7. Puppet Enterprise
Puppet Enterprise is an agent-based configuration management platform designed for automating, securing, and enforcing desired state configurations across large-scale infrastructure. While often categorized separately, it functions as one of the foundational cloud infrastructure automation tools, especially for managing the lifecycle of servers, applications, and services in complex, hybrid environments. Its strength lies in its model-driven approach, which abstracts away system-level details to provide a declarative way to manage systems at scale.
This platform excels in regulated industries where continuous compliance and auditability are paramount. Puppet enforces a desired state, automatically remediating any configuration drift to ensure systems remain consistent and compliant with defined policies. Its robust reporting capabilities provide deep visibility into infrastructure changes, making it invaluable for security audits and operational stability in enterprise settings.

Key Considerations
Puppet’s agent-based architecture ensures that every node continuously checks in and maintains its prescribed state, making it highly reliable for mission-critical systems.
| Feature | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Node-based licensing, where costs are tied to the number of managed nodes. This model requires careful capacity planning and can become expensive for highly elastic environments with ephemeral nodes. |
| Deployment Options | Primarily self-hosted, giving organizations complete control over their automation environment. This is ideal for air-gapped networks or environments with strict data residency requirements. |
| Ecosystem & Integration | Features a mature ecosystem with thousands of pre-built modules on the Puppet Forge, accelerating development for common technologies. It integrates well with CI/CD tools, cloud platforms, and other DevOps solutions. |
| Use Case Focus | Excels at configuration management and continuous compliance. It is often paired with provisioning tools like Terraform, where Terraform creates the infrastructure and Puppet configures and maintains it post-deployment. |
Practical Tip: Leverage the Role and Profile pattern to structure your Puppet code. This design pattern separates business logic (Roles) from technical implementation (Profiles), making your codebase more modular, reusable, and easier to manage as your infrastructure grows. You can explore how it compares to other tools and learn more about Puppet Enterprise on opsmoon.com.
Website: https://www.puppet.com/downloads/puppet-enterprise
8. Progress Chef (Chef Enterprise Automation Stack / Chef Infra)
Progress Chef is a comprehensive policy-as-code platform that extends beyond basic provisioning to cover infrastructure configuration, continuous compliance, and application delivery automation. As one of the more mature cloud infrastructure automation tools, Chef excels in environments requiring strict, auditable policy enforcement from development through production. Its core strength lies in its "cookbook" and "recipe" model, which allows teams to define system states declaratively and enforce them consistently across hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
The platform is particularly well-suited for organizations that prioritize a test-driven approach to infrastructure. With Chef InSpec, its integrated compliance-as-code framework, teams can define security and compliance rules as executable tests. This enables continuous auditing against policies, ensuring that infrastructure remains in its desired state and meets regulatory requirements at all times. The Enterprise Automation Stack unifies these capabilities with SaaS dashboards and job orchestration for centralized management.
Key Considerations
Chef's agent-based architecture ensures that nodes continuously converge to their defined state, making it a powerful tool for managing large, complex server fleets.
| Feature | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Primarily node-based with tiered pricing available through AWS Marketplace. Official pricing is not transparent on their website, typically requiring a direct sales quote, which can be a hurdle for initial evaluation. |
| Deployment Options | Available as a fully managed SaaS platform (Chef SaaS) or a self-managed installation. Procurement directly through the AWS Marketplace simplifies purchasing for organizations already in that ecosystem. |
| Ecosystem & Integration | Integrates deeply with compliance and security workflows via Chef InSpec. The Chef Supermarket provides a vast repository of community and official cookbooks to accelerate development and reuse common configurations. |
| Onboarding Experience | The learning curve can be steeper compared to pure IaC tools like Terraform. Mastering its Ruby-based DSL and concepts like recipes, cookbooks, and run-lists requires a more significant initial investment from engineering teams. |
Practical Tip: Leverage the test-kitchen tool extensively in your local development workflow before pushing cookbooks to production. This allows you to test your infrastructure code in isolated environments, ensuring recipes are idempotent and behave as expected across different platforms.
Website: https://www.chef.io/products/enterprise-automation-stack
9. Salt Project (open source) / Tanzu Salt (enterprise)
Salt Project is a powerful open-source platform specializing in event-driven automation, remote execution, and configuration management. Acquired by VMware and now part of the Tanzu portfolio for its enterprise offering, Salt stands out among cloud infrastructure automation tools for its high-speed data bus and ability to manage massive, distributed fleets of servers, from data centers to edge devices. Its core strength is managing infrastructure state and executing commands on tens of thousands of minions simultaneously.
The platform is ideal for teams needing real-time infrastructure visibility and control, especially in hybrid or multi-cloud environments. Salt’s event-driven architecture allows it to react automatically to changes, making it excellent for self-healing systems and complex orchestration workflows. Unlike agentless tools that rely on SSH, Salt's persistent minion agent enables a fast and secure communication channel, providing immediate remote execution capabilities.
Key Considerations
Salt's YAML-based state files are declarative, but its architecture also supports imperative execution, offering a unique blend of control for complex tasks.
| Feature | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Pricing Model | The core Salt Project is free and open source. The enterprise version, VMware Tanzu Salt, is commercially licensed, with pricing based on the number of managed nodes and support level. |
| Deployment Options | Primarily self-hosted, giving organizations complete control. Tanzu Salt provides enterprise binaries and support for on-premises or private cloud deployments. |
| Ecosystem & Integration | Integrates well with various cloud providers and infrastructure components. The "Salt Reactor" system can trigger actions based on events from third-party tools, creating a highly responsive automation fabric. |
| Licensing | Salt Project is licensed under Apache 2.0, a permissive open-source license. Tanzu Salt follows VMware's commercial licensing model. |
Practical Tip: Leverage Salt's event-driven "Reactor" and "Beacon" systems to build self-remediating infrastructure. For example, configure a beacon to monitor a critical service and a reactor to automatically restart it if it fails, reducing manual intervention.
Website: https://saltproject.io/
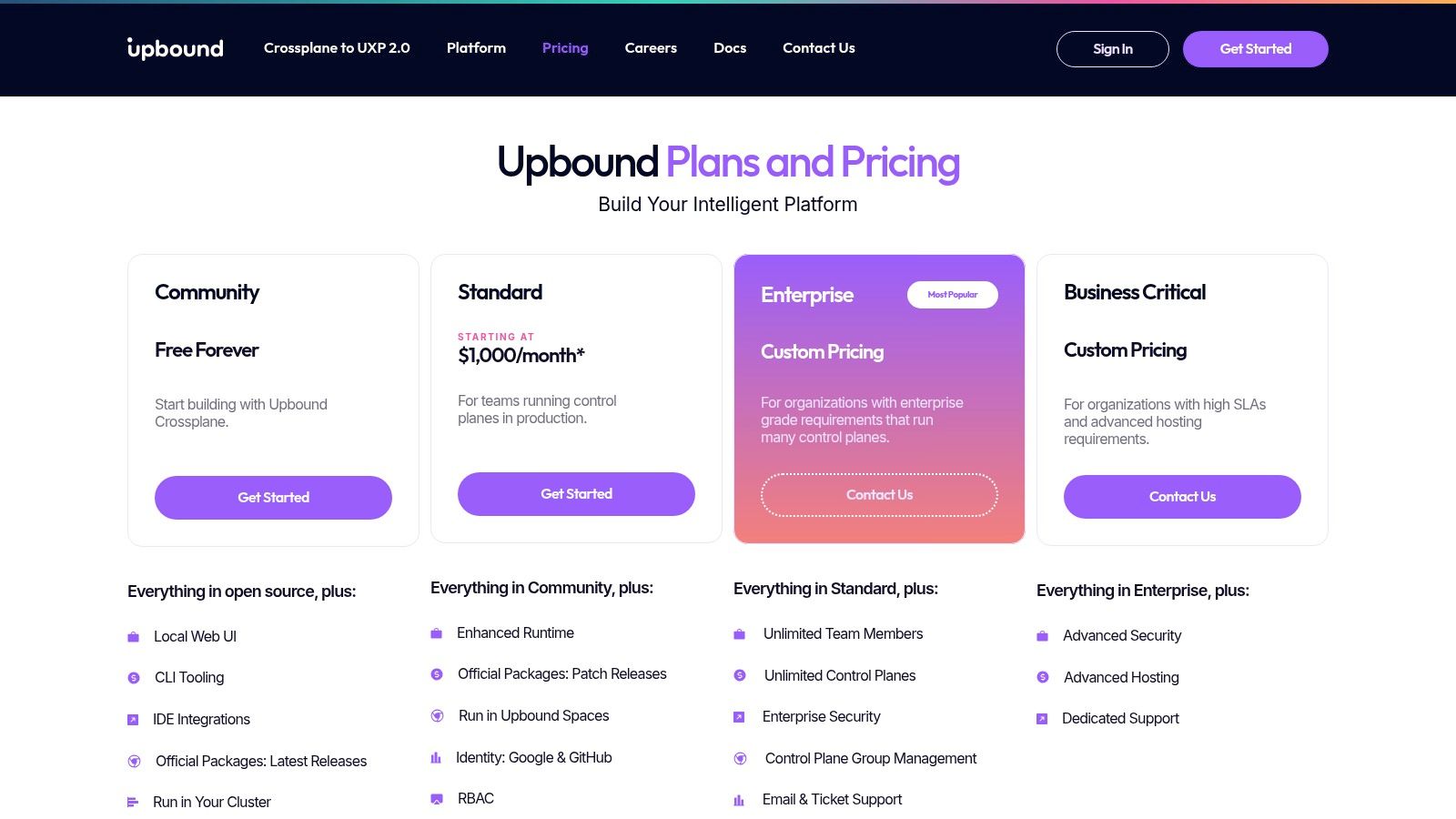
10. Upbound (Crossplane)
Upbound is a commercial platform built upon the open-source Crossplane project, offering managed control planes for cloud-native platform engineering. It extends Kubernetes to manage and compose infrastructure from multiple vendors, solidifying its place among modern cloud infrastructure automation tools. Upbound's core strength is enabling platform teams to build their own internal cloud platforms with custom, high-level abstractions, providing developers with a self-service experience to provision the infrastructure they need without deep cloud-specific knowledge.
This approach is ideal for organizations building "golden paths" for their development teams, abstracting away the complexity of underlying cloud services. By defining a custom set of APIs (Composite Resources), platform engineers can present developers with simple, policy-compliant infrastructure building blocks. This significantly reduces cognitive load on developers and enforces organizational standards for security, compliance, and cost management directly within the Kubernetes ecosystem.
Key Considerations
The platform provides a UI, identity and RBAC layer, and a marketplace for official provider packages, streamlining the operational management of Crossplane.
| Feature | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Consumption-based, billed by managed resources. Different tiers (Community, Standard, Enterprise) offer varying levels of support and features. |
| Deployment Options | Offered as a fully managed SaaS platform. The underlying Crossplane project can be self-hosted, but Upbound provides the managed control plane experience. |
| Ecosystem & Integration | Leverages the Crossplane provider ecosystem, which is growing rapidly and supports all major clouds and many other cloud-native services. |
| Learning Curve | The control plane and Composition model is powerful but introduces new concepts. Teams familiar with Kubernetes will adapt faster, but it requires a shift in thinking. |
Practical Tip: Start by identifying one or two high-value, frequently provisioned resources (like a database or a Kubernetes cluster) to build your first Composite Resource Definition (XRD). This allows your team to learn the composition model with a tangible, useful abstraction before scaling it out to your entire infrastructure catalog.
Website: https://www.upbound.io/pricing
11. AWS Marketplace — Infrastructure as Code category
AWS Marketplace serves as a centralized procurement hub, offering a curated catalog of third-party cloud infrastructure automation tools that can be deployed directly into an AWS environment. Instead of being a single tool, it's a discovery and purchasing platform where you can find, subscribe to, and manage solutions like Ansible Tower, Chef Automate, and various Terraform-adjacent platforms. Its primary value is streamlining the acquisition process by integrating billing directly into your existing AWS account.
This platform is ideal for organizations deeply embedded in the AWS ecosystem that want to simplify vendor management and leverage existing AWS Enterprise Discount Programs (EDP). It eliminates the need to set up separate contracts and billing relationships with each tool provider. For engineering leaders, this means faster access to necessary tools, allowing teams to experiment with and adopt new automation technologies without prolonged procurement cycles.
Key Considerations
The user experience focuses on discovery and one-click deployment, often providing pre-configured AMIs or CloudFormation templates to accelerate setup.
| Feature | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Varies by vendor. Options include free trials, bring-your-own-license (BYOL), hourly/annual subscriptions, and metered usage, all consolidated into a single AWS bill. |
| Deployment Options | Most listings are deployed as AMIs, CloudFormation stacks, or SaaS subscriptions directly from the marketplace, ensuring tight integration with the AWS environment. |
| Ecosystem & Integration | The catalog is extensive, featuring established vendors and niche solutions. It allows organizations to build a best-of-breed automation stack using pre-vetted software. |
| Procurement Efficiency | Standardized contracts and private offer capabilities simplify negotiation and purchasing, making it a powerful tool for enterprise procurement and finance teams. |
Practical Tip: Before subscribing, carefully evaluate each marketplace offering's support model and versioning. Some third-party listings may lag behind the latest official releases, which could impact access to new features or security patches. Always check the "Usage Information" and "Support" sections on the product page.
Website: https://aws.amazon.com/marketplace/solutions/devops/infrastructure-as-code
12. Azure Marketplace and consulting offers for IaC
The Azure Marketplace serves as a centralized hub for organizations to discover, procure, and deploy software and services optimized for the Azure cloud. While not a standalone tool, it's a critical resource for finding pre-packaged cloud infrastructure automation tools, solutions, and expert consulting services. It simplifies the adoption of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) by offering ready-to-deploy Terraform and Bicep templates, along with professional services for custom implementations and workshops.
This platform is ideal for teams deeply integrated into the Microsoft ecosystem. Its key advantage is procurement efficiency; purchases can often be applied toward an organization's Azure Consumption Commitment (MACC) and are consolidated into a single Azure bill. This streamlines vendor management and budgeting, making it easier to engage specialized partners for complex IaC projects without lengthy procurement cycles.
Key Considerations
The user experience is geared towards discovery and procurement, requiring users to filter through a mix of software listings and consulting offers to find the right fit.
| Feature | Analysis |
|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Varies widely by listing. Includes free templates, BYOL (Bring Your Own License) software, and fixed-price or custom-quoted consulting engagements. |
| Deployment Options | Offers direct deployment of virtual machine images, applications, and IaC templates from the marketplace into your Azure environment. |
| Ecosystem & Integration | Tightly integrated with Azure services, billing, and identity management (Azure AD). Offers solutions from Microsoft partners and third-party vendors. |
| Quality & Scope | The quality and depth of consulting offers can differ significantly between partners, necessitating careful vetting of provider credentials and project scopes. |
Practical Tip: Use the "Consulting Services" filter and search for specific keywords like "Terraform" or "Bicep" to narrow down the listings. Always review the partner's case studies and request a detailed statement of work before committing to a private offer.
Website: https://azuremarketplace.microsoft.com/en-us
Cloud Infrastructure Automation Tools Comparison
| Solution | Core Features | User Experience & Quality Metrics | Value Proposition | Target Audience | Price Points & Licensing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBM HashiCorp Cloud Platform (HCP Terraform) | Managed Terraform, state mgmt, RBAC, policy | Mature workflows, enterprise SSO, broad provider ecosystem | Enterprise-grade Terraform standardization | Large enterprise teams | Usage-based (Resources Under Management), vendor-licensed core |
| Pulumi (IaC + Pulumi Cloud) | Multi-language IaC, state, policy, drift detection | Developer-friendly, app stack integration | Flexible IaC with general-purpose languages | Developers integrating IaC | Per-resource billing, generous free tier |
| AWS CloudFormation | AWS resource provisioning, drift detection | Deep AWS integration, no extra AWS cost | Native AWS IaC service with comprehensive resource support | AWS users & teams | No additional AWS cost, charges for 3rd-party hooks |
| Microsoft Azure Bicep (ARM) | DSL compiling to ARM templates, what-if planning | Simpler syntax, state stored by Azure | Free, tightly integrated Azure IaC | Azure-focused teams | Free tool, pay for Azure resources |
| Google Cloud Infrastructure Manager (Terraform) | Native Terraform on GCP, GitOps, policy | Native GCP integration, clear cost model | Managed Terraform runs on Google Cloud | GCP users | Cost based on Cloud Build minutes & storage |
| Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform | Automation Hub, certified content, cloud integrations | Strong Linux heritage, event-driven automation | Hybrid cloud automation & configuration management | Enterprise Linux/infra teams | Quote-based pricing, capacity estimate |
| Puppet Enterprise | Declarative config mgmt, compliance reporting | Proven in regulated environments | Large fleet config mgmt & compliance | Large regulated orgs | Node-based licensing, quote-based |
| Progress Chef (Enterprise Automation Stack) | Policy-as-code, compliance, SaaS/self-managed | Mature policy tooling, SaaS dashboards | Automation across infrastructure & apps | Organizations standardizing compliance | Tiered node-based pricing, quote required |
| Salt Project / Tanzu Salt | Remote execution, event-driven automation | Highly flexible, active open-source community | Open-source config mgmt with VMware support | Open-source community & enterprises | Free open-source, VMware subscription for enterprise |
| Upbound (Crossplane) | Multi-cloud control plane, RBAC, packages | Platform engineering model, multi-cloud ready | Managed self-service infrastructure platform | Platform engineering teams | Consumption-based by resources, multiple editions |
| AWS Marketplace – IaC category | Variety of IaC tools, private offers | Simplified billing & procurement | Centralized access to IaC solutions on AWS | AWS customers & enterprise buyers | Variable by vendor, consolidated AWS billing |
| Azure Marketplace & consulting offers for IaC | Software & consulting, Terraform/Bicep packages | Consolidated billing, curated consulting | Marketplace for IaC software & expert services | Azure users & enterprises | Mixed pricing; software plus consulting fees |
Synthesizing Your Strategy: From Tools to an Automated Ecosystem
We have navigated the complex and dynamic landscape of modern cloud infrastructure automation tools, from declarative giants like Terraform and Pulumi to configuration management mainstays such as Ansible and Puppet. Each tool presents a unique philosophy, a distinct set of capabilities, and a specific position within the broader DevOps toolchain. The journey from manual infrastructure provisioning to a fully automated, scalable, and resilient ecosystem is not about picking a single "best" tool. Instead, it is about strategically assembling a complementary toolkit that aligns with your organization's technical stack, operational maturity, and strategic goals.
The central theme emerging from our analysis is the convergence of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and configuration management. Tools like Terraform and CloudFormation excel at provisioning the foundational resources-VPCs, subnets, Kubernetes clusters, and databases. In contrast, Ansible, Chef, and Salt specialize in the fine-grained configuration of those resources after they exist-installing software, managing user accounts, and enforcing security policies. A mature automation strategy recognizes this distinction and leverages the right tool for the right job, creating a seamless pipeline from bare metal (or its cloud equivalent) to a fully configured, application-ready environment.
Key Takeaways and Strategic Considerations
Moving forward, your selection process should be guided by a methodical evaluation of your specific context. Avoid the trap of choosing a tool based on popularity alone. Instead, consider these critical factors:
- Declarative vs. Procedural: Do your teams prefer to define the desired end state (declarative, like Terraform or Pulumi) or to script the explicit steps to reach that state (procedural, like Ansible or Chef)? Declarative models are often better for managing complex, interdependent cloud resources, while procedural approaches can offer more granular control for server configuration.
- Language and Skillset: The choice between a Domain-Specific Language (DSL) like HCL (Terraform) or Bicep versus a general-purpose programming language like Python, Go, or TypeScript (Pulumi) is fundamental. A general-purpose language lowers the barrier to entry for development teams and enables powerful abstractions, but a DSL provides a more focused, purpose-built syntax that can be easier for operations-focused teams to adopt.
- State Management: How a tool tracks the state of your infrastructure is a crucial operational concern. Terraform's state file is both its greatest strength (providing a source of truth) and a potential bottleneck. Managed services like HCP Terraform Cloud or Pulumi Cloud abstract this complexity away, offering collaborative features that are essential for growing teams.
- Ecosystem and Integration: No tool operates in a vacuum. Evaluate the provider ecosystem and community support. How well does the tool integrate with your chosen cloud provider (AWS, Azure, GCP), your CI/CD system (Jenkins, GitLab CI, GitHub Actions), and your observability stack? A rich ecosystem of modules, plugins, and integrations will significantly accelerate your automation efforts.
Actionable Next Steps: Building Your Automation Roadmap
Translating this knowledge into action requires a structured approach. Your immediate next steps should not be to rip and replace existing systems but to build a strategic roadmap for incremental adoption.
- Conduct a Technology Audit: Catalog your current infrastructure and identify the most painful, error-prone, and time-consuming manual processes. These are your prime candidates for initial automation projects.
- Define a Pilot Project: Select a small, non-critical service or environment. Use this pilot to build a proof-of-concept with one or two shortlisted cloud infrastructure automation tools. This hands-on experience is invaluable for understanding the real-world complexities and workflow implications.
- Invest in Team Enablement: Your tools are only as effective as the people who use them. Allocate time and resources for training, workshops, and creating internal documentation and best practices. Foster a culture of "everything as code" to ensure long-term success.
- Think in Layers: Design your automation strategy in layers. Use a foundational IaC tool (e.g., Terraform) for core infrastructure, a configuration management tool (e.g., Ansible) for application setup, and potentially a specialized tool like Crossplane to create a unifying platform API for developers.
Ultimately, the goal is to build an integrated, automated ecosystem, not just a collection of disparate tools. By carefully selecting and combining these powerful solutions, you can create a robust, self-healing infrastructure that empowers your development teams, enhances security, and provides the scalable foundation needed to drive business innovation.
Navigating the complexities of these cloud infrastructure automation tools and integrating them into a cohesive strategy can be a significant challenge. OpsMoon provides on-demand, expert DevOps and SRE talent to help you design, build, and manage your ideal automation ecosystem without the overhead of full-time hires. Accelerate your DevOps journey by connecting with our vetted freelance experts at OpsMoon.
